People often get confused when they hear about Router and Modem. These two devices are essential for a good broadband experience. Most of the people, in this confusion, often end up assuming both to be the same when that’s not the case. Read this article, and we are confident that the mist of confusion will be eliminated from your brain.
Router VS Modem: The Differences!
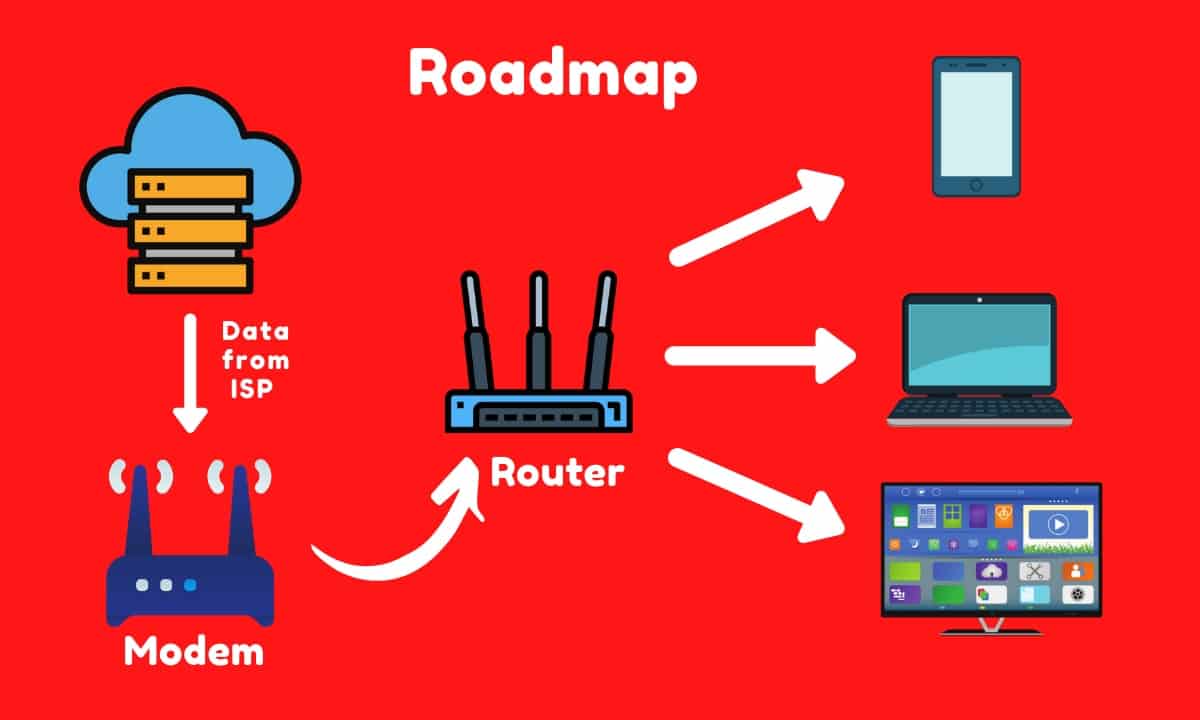
A modem is more like a translator that helps you talk to people who don’t know your language. Here, the “people” are the Internet. A modem reads the data coming from your ISP and converts it into a format (a stream of 0’s and 1’s) that the majority of electronic devices understand.
Whereas, the Router acts as a merchant that takes the data from the Modem and sends it to devices. A router can also receive data from the connected devices and send it to the Modem, back to the ISP (in this way, ISP’s can track your search history).
ALSO READ: What Is WEP, WPA, WPA2, And WPA3? Where Do Your Wi-Fi Security Stand? [Explained]
People use both together for the best experience— the Modem acts as a medium to establish a connection between the Router and the ISP. The Router distributes the data across various devices at your home.
What Is A Modem?
A modem’s work is to convert the data from your ISP to binary language that your computer can recognize. Similarly, it can record your actions and send them to ISPs. Usually, our homes are connected to the ISPs via copper cables or phone lines. Unlike fiber optic cables that use digital signals, these don’t. So, you don’t need to worry about your data being compromised.
Copper cables use electricity, whereas phone lines use analog signals. The Modem needs to convert these signals to digital, and vice versa. The act of turning digital to analog and vice-versa is called “modulating” and “demodulating”.
What Is A Router?
A router transfers data coming from the Modem to various devices. Plugin the ethernet cable, and you can enjoy surfing the Internet by connecting to a 2.4 or 5Ghz network band. However, some routers have firewalls to keep the connections secure. Modern-day routers allow you to add VPN details in the settings, and it automatically routes the links towards the VPN’s servers.
ALSO READ: 5 Best Free VPNs That You Can Use In 2020 [Best-Of-The-Best]
The New Kid In The House
Fiber optic cable is another medium by which the data can be transferred. They work on the mechanism called “Total Internal Reflection.” In this, light acts as a source of data. When sent through the wire, it collides with the walls of the wire and reflects further. Hence, the loss of data is minimized, and the bandwidth is increased.
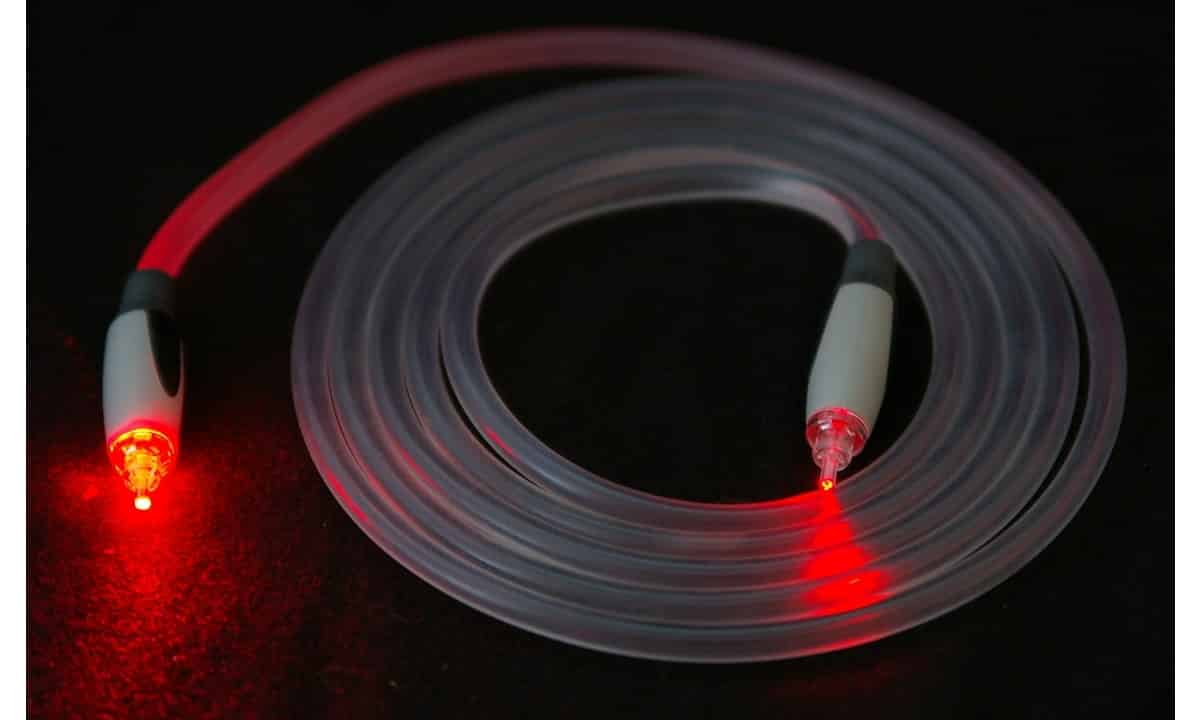

Fiber-optic connections do not get into the home directly. They travel the majority of the way, and then the regular cables carry the rest of the work. These cables carry signals that also need translating when they arrive.
You might be wondering about connecting the Modem directly to your computer via the ethernet port. Yes, you can do that but, remember, this way, you’ll not be secure.
Summing Up
The Modem acts as a translator between the Router and the ISP, whereas, the Router, as the name suggests, transmits the decoded data to different devices connected to the Router. We hope this router vs modem article clears all your doubts, but if you have any left, let us know in the comment section below.
BONUS VIDEO
For the latest tech news, follow TechDipper on Twitter, Facebook, Telegram, Instagram, and subscribe to our YouTube channel.